The Angular observable Map operator takes an observable source as input. It applies a project function to each of the values emitted by the source observable and transforms them into a new value. It then emits the new value to the subscribers. We use an angular map operator with a Pipe, which allows us to chain multiple operators together. In this guide, we’re going to learn how to use the Map operator with examples like converting the source to upper case, using Map with the Angular HTTP Request, with DOM events, filtering the input data, and using multiple Map Operators together, etc.
Table of Contents
Syntax
The syntax of the map operator is as follows:
1 2 3 | map<T, R>(project: (value: T, index: number) => R, thisArg?: any): OperatorFunction<T, R> |
project: is a function that we use to manipulate the values emitted by the source observable. The project can accept two arguments. One is value i.e., the value emitted by the observable. The second argument is the index number. The index number starts with 0 for the first value emitted and is incremented by one for every subsequent value emitted. It is similar to the index of an array.
thisArg: is optional and default is undefined. It defines what this is in the project function.
Using Observable Map
To use map first, we need to import it from the rxjs/operators library.
1 2 3 | import { map } from 'rxjs/operators' |
Next, create an observable from an array of numbers as shown below.
1 2 3 | srcArray = from([1, 2, 3, 4]); |
Use the pipe method to invoke the map method.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | multiplyBy2() { this.srcArray .pipe(map(val => { return val * 2})) .subscribe(val => { console.log(val)}) } |
The project function accepts only one argument val and returns it multiplied by 2.
1 2 3 | map(val => { return val * 2}) |
Finally, we subscribe and print the result in the console. The output is 2,4,6,8
The following image explains how values from the source observable ( i.e.1,2,3,4 ) go through the map which transforms it into new values by multiplying it by 2.
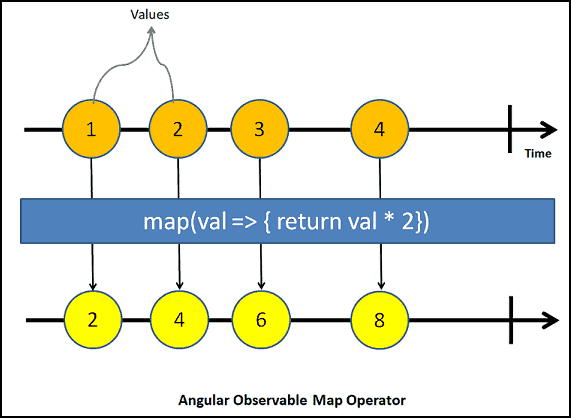
You can also access the second argument index as shown below. It starts as 0 for the first value and gets incremented for every subsequent value.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | multiplyBy2() { this.srcArray .pipe(map((val, i) => { //index console.log(i) //0 return val * 2; })) .subscribe(val => { console.log(val) }) } |
Map Examples
Convert input to upper-case
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | srcName$ = from(['John', 'Tom', 'Katy']) toUpperCase() { this.srcName$ .pipe(map(data => { return data.toUpperCase(); })) .subscribe(data => console.log(data)) } |
Map to a Single Property
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | srcObject = from([ { fName: 'Sachin', lName: "Tendulkar" }, { fName: 'Rahul', lName: "Dravid" }, { fName: 'Saurav', lName: "Ganguly" }, ]); MapToSingleProperty() { this.srcObject .pipe(map(data => { return data.fName + ' ' + data.lName })) .subscribe(data => { console.log(data) }) } //output Sachin Tendulkar Rahul Dravid Saurav Ganguly |
Using Map with HTTP Request
The following code gets the list of dogs breeds from the https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/list/all API and uses the keyValue pipe to transform the object into an array of key-value pairs.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | import { Component, OnInit, ViewChild, ElementRef } from '@angular/core'; import { Observable, from, pipe, fromEvent } from 'rxjs'; import { map, filter, tap } from 'rxjs/operators' import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; import { KeyValuePipe } from '@angular/common'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'], providers: [KeyValuePipe] }) export class AppComponent implements OnInit { constructor(private http: HttpClient, private keyValue: KeyValuePipe) { } @ViewChild('btn', { static: true }) button: ElementRef; $dogsBreed(): Observable<any> { return this.http.get<any>("https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/list/all") } getDogsBreed() { this.$dogsBreed() .pipe(map(data => { var dogs = this.keyValue.transform(data.message) console.log(dogs) })) .subscribe(); } } |
Using with event
You can create observable from event and use the map to transform the values.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | buttonClick() { fromEvent(this.button.nativeElement, 'click') .pipe(map( ev => (ev as any).clientX)) .subscribe(res => console.log(res)); } |
map with filter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | srcArray = from([1, 2, 3, 4]); filterWithMap() { this.srcArray .pipe( filter(val => { return val > 2; }), map((val, i) => { return val * 2; })) .subscribe(val => { console.log(val) }) } |
Multiple map
The following examples show the use of multiple map functions. The first map adds 10, while the second mad multiplies by 2.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | mulitpleMaps() { this.srcArray .pipe( map(val => { return val + 10; }), map((val, i) => { return val * 2; })) .subscribe(val => { console.log(val) }) } |
References
Read More



Add HttpClientModule into app.module.ts file if have error when run example map with http request
Add HttpClientModule into app.module.ts file if have error when run example map with http request
you could have given better examples, though it is good for beginners to understand