In this Angular Services tutorial, we will show you how to build a simple component that fetches a
Table of Contents
What is an Angular Service
Service is a piece of reusable code with a focused purpose. A code that you will use in many components across your application
Our components need to access the data. You can write data access code in each component, but that is very inefficient and breaks the rule of single responsibility. The Component must focus on presenting data to the user. The task of getting data from the back-end server must be delegated to some other class. We call such a class a Service class. Because it provides the service of providing data to every component that needs it.
What Angular Services are used for
- Features that are independent of components such a logging services
- Share logic or data across components
- Encapsulate external interactions like data access
Advantageous of Angular Service
- Services are easier to test.
- They are easier to Debug.
- We can reuse the service at many places.
How to create a Service in Angular
An Angular service is simply a Javascript function. All we need to do is to create a class and add methods & properties. We can then create an instance of this class in our component and call its methods.
One of the best uses of services is to get the data from the data source. Let us create a simple service, which gets the product data and passes it to our component.
You can download the source code from stackBlitz
Product Model
Create a new file under the folder src/app and call it product.ts
product.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | export class Product { constructor(productID:number, name: string , price:number) { this.productID=productID; this.name=name; this.price=price; } productID:number ; name: string ; price:number; } |
The Product class above is our domain model.
Product Angular Service
Next, let us build an Angular Service, which returns the list of products.
Create a new file under the folder src/app and call it product.service.ts
product.service.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import {Product} from './product' export class ProductService{ public getProducts() { let products:Product[]; products=[ new Product(1,'Memory Card',500), new Product(1,'Pen Drive',750), new Product(1,'Power Bank',100) ] return products; } } |
First, we import the Product model from the product.ts
Next, create ProductService class and export it. We need to export so that the Components & Other service class import it and use it
The getProducts method returns the collection of the products. In this example, we have hardcoded the products. In real life, you would send an HTTP GET request to your back end API to get the data
Now our service is ready.
Note that the above class is a simple JavaScript function. There is nothing Angular about it.
Invoking the ProductService
The Next step is to invoke the ProductService from the component. Open the app.componet.ts and add the following code.
app.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Product } from './product'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', }) export class AppComponent { products:Product[]; productService; constructor(){ this.productService=new ProductService(); } getProducts() { this.products=this.productService.getProducts(); } } |
We start with importing Product & ProductService
We create an instance of ProductSerivce in the constructor of the AppComponet. In real-life Angular Apps, we use the Dependency Injection in Angular to inject the ProductSerivce in the constructor. We will learn that in the next tutorial.
The getProducts method calls the getProducts method of the ProductService. It returns a list of Products, which we store in the local variable products
Template
The next step is to display the Products to user
Open the app.component.html file and add the following code
app.componenet.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | <div class="container"> <h1 class="heading"><strong>Services </strong>Demo</h1> <button type="button" (click)="getProducts()">Get Products</button> <div class='table-responsive'> <table class='table'> <thead> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Price</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr *ngFor="let product of products;"> <td>{{product.productID}}</td> <td>{{product.name}}</td> <td>{{product.price}}</td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> </div> |
We are using the bootstrap 4 to style our template here. You will find the link in the index.html.
The button Get Products, calls the getProducts method of the component class via event binding
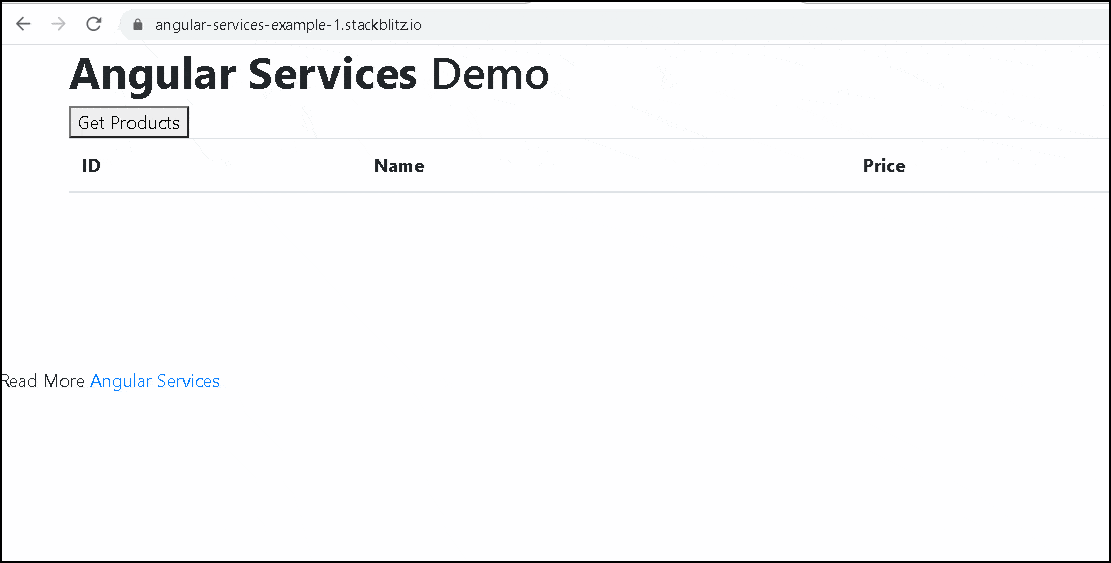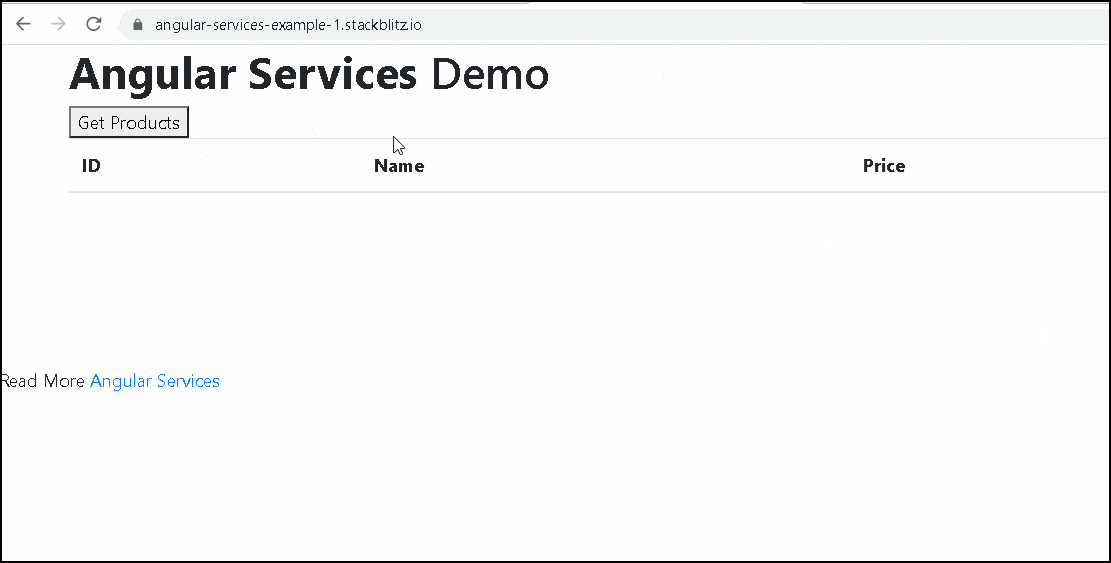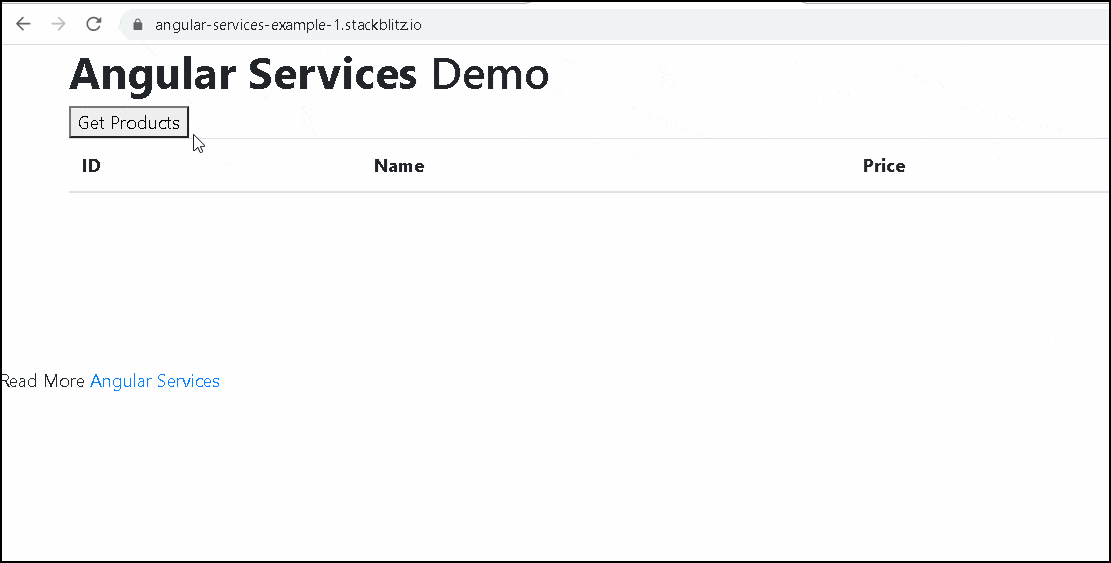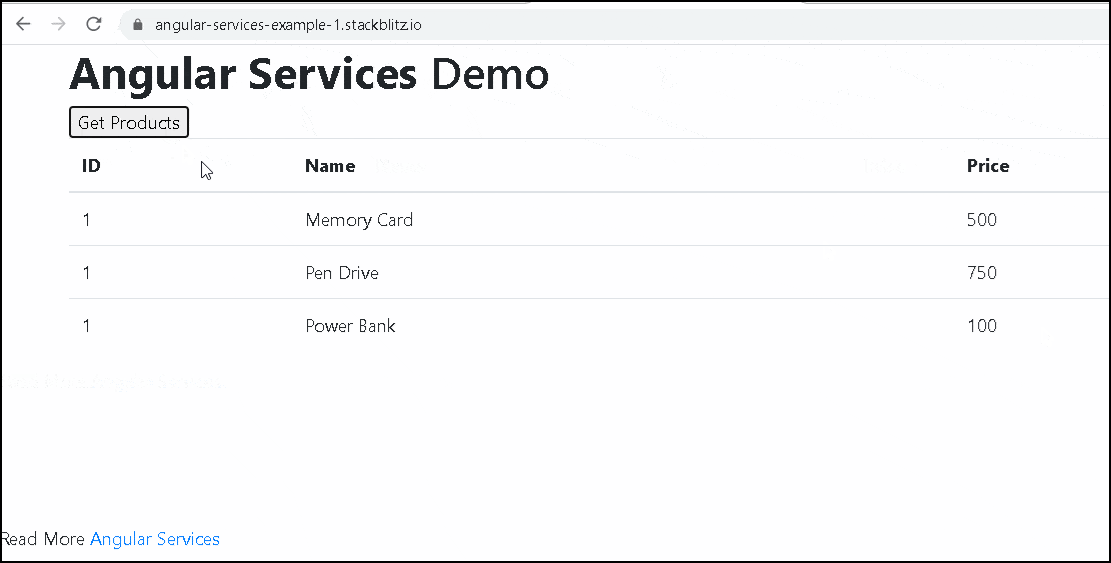
We loop through the products via ngFor directive and display it in a table.
Now, you can run the code and click on the Get Product button. You will see the List of Products
Injecting Services into Component
In the example, we instantiated the productService in the Component directly as shown below
1 2 3 | this.productService=new ProductService(); |
Directly instantiating the service, as shown above, has many disadvantageous
- The
ProductServiceis tightly coupled to the Component. If we change theProductServiceclass definition, then we need to update every code where service is used - If we want to change
ProductServicewithBetterProductService, then we need to search wherever theProductServiceis used and manually change it - Makes Testing difficult. We may need to provide
mockProductServicefor testing and use theProductServicefor Production.
We can solve this by using the Angular Dependency injection, which is our next tutorial.
References
Read More
- Angular Tutorial
- Services
- Dependency injection
- Injector, @Injectable & @Inject
- Providers
- Injection Token
- Hierarchical Dependency Injection
- Angular Singleton Service
- ProvidedIn root, any & platform
- @Self, @SkipSelf & @Optional Decorators
- @Host Decorator in Angular
- ViewProviders
- Introduction to Angular Modules
- Lazy Loading in Angular
- Preloading Strategy



eefed
s
Awesome content using that I am learning Angular.